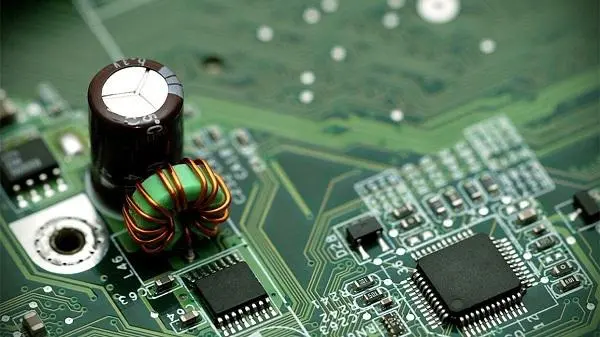
As the carrier of various PCB components and the hub of circuit signal transmission, PCB has become the most important and crucial part of electronic information products. The quality and reliability of PCB determine the quality and reliability of the whole equipment. However, due to cost and technical reasons, a large number of failures occurred in the production and application of PCB.
For this kind of fault problem, we need to use some common fault analysis PCB technologies to ensure the quality and reliability level of PCB in the manufacturing process. Ten main fault analysis techniques are summarized for reference.

1. Appearance inspection
Visual inspection is to check the appearance of PCB by visual inspection or using some simple instruments (for example, stereomicroscope, metallographic microscope and even magnifying glass) to find part faults and relevant physical evidence. The main function is to locate the fault and preliminarily determine the fault mode of PCB. Appearance inspection mainly checks PCB contamination, corrosion, explosive plate position, circuit wiring and fault regularity. If it is batch or single, it is always concentrated in a certain area. In addition, there are many PCB faults that can only be found after the PCBA is assembled. Whether the failure is caused by the assembly process and the influence of materials used in the process also requires careful inspection of the characteristics of the failure area.
2. X-ray fluoroscopy
For some parts that cannot pass the visual inspection, as well as through holes and other internal defects inside the PCB, we must use the X-ray fluoroscopy inspection system to check. The X-ray fluoroscopy system uses different material thicknesses or different material densities to absorb X-ray or transmit light through different principles. This technology is more used to check the internal defects of PCBA solder joints, the internal defects of through-hole and the locations of defective solder joints of high-density BGA or CSP devices. The resolution of current industrial X-ray fluoroscopy equipment can be less than one micron, and it has been transformed from two-dimensional imaging equipment to three-dimensional imaging equipment. Even five dimensional (5D) equipment has been used for packaging inspection, but this 5D X fluoroscopy system is very expensive and rarely used in industry.
3. Slice analysis
Slice analysis is a series of methods and steps (such as sampling, inlaying, slicing, polishing, corrosion, and observation). Through slice analysis, you can obtain rich information about PCB microstructure (through-hole, electroplating, etc.), which provides a good basis for the next step of quality improvement. However, this approach is destructive. After slicing, the sample will be destroyed. At the same time, this method requires a lot of sample preparation, and sample preparation takes a long time, which requires well-trained technicians to complete. For detailed slicing procedures,
4. Scanning acoustic microscope
At present, C-mode ultrasonic scanning acoustic microscope is mainly used for electronic packaging or assembly analysis. It uses high-frequency ultrasonic reflection on the discontinuous interface between material and phase and pole. The imaging method is based on the change of the image, while the scanning method scans the information in the XY plane along the Z axis. Therefore, scanning acoustic microscopy can be used to detect various defects in components, materials, PCB and PCBA, including cracks, delaminations, inclusions and voids. If the frequency width of the scanning sound is large enough, the internal defects of the solder joint can also be directly detected. The typical scanning sound image is red warning color, indicating the existence of defects. Because many plastic encapsulated components are used in the SMT process, there will be a lot of problems sensitive to moisture backflow in the process of converting lead to lead-free. That is, when the hygroscopic plastic packaging device is refluxed at a higher lead-free process temperature, it will have the phenomenon of internal or substrate delamination cracking, and the ordinary PCB is often cracked at the high temperature of the lead-free process. At this time, scanning acoustic microscope highlights its special advantages in nondestructive testing of multilayer high-density PCB. In general, visible broken plates can only be found by visual inspection.
5. Micro infrared analysis
Micro infrared analysis is an analysis method combining infrared spectrum and microscope. It uses different materials (mainly organic substances) to absorb infrared spectra with different absorptivity. Principle: analyze the chemical composition of the material, and combine the microscope to make visible light and infrared light have the same light path. As long as in the visible field of vision, trace organic pollutants can be found for analysis. If the microscope is not used, usually the infrared spectrum can only analyze a large number of samples. In many cases of electronic process, trace contamination will lead to poor solderability of PCB pads or pins. It can be imagined that it is difficult to solve the process problem without the infrared spectrum of the microscope. The main purpose of micro infrared analysis is to analyze the organic pollutants on the welding surface or joint surface, and analyze the causes of corrosion or poor weldability.