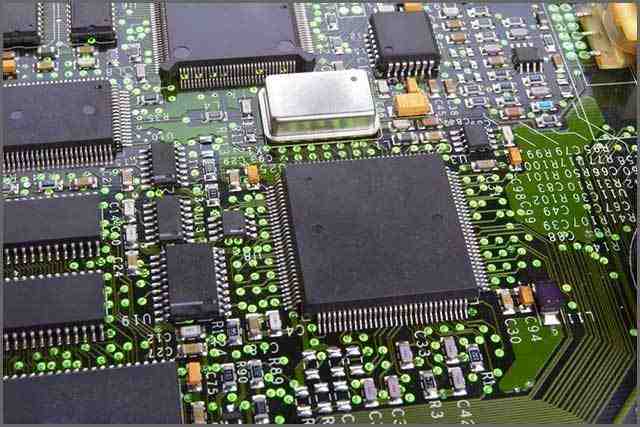
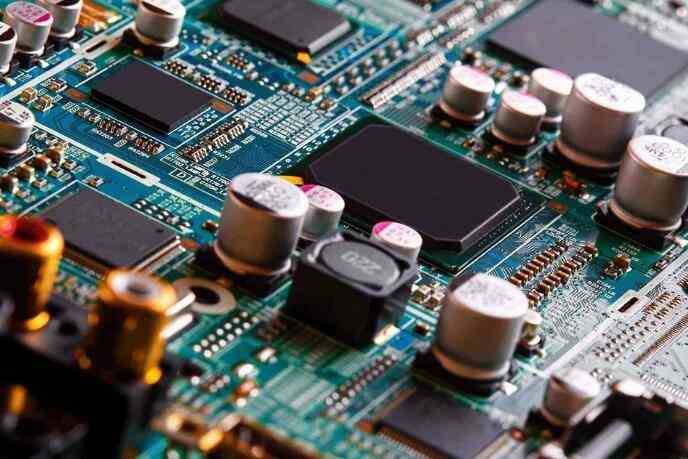
The life and performance of circuit board machining depend on the selection of PCB board. In order to select the right PCB board, you need to know the materials used in the different board classes. Understanding the electrical and physical characteristics of different PCB boards helps to select boards for PCB machining.
Board spacing and width are also important when dealing with large amounts of current. The structural strength of the circuit board is determined by the substrate and laminate. The material choice for these two layers depends on the type of board.
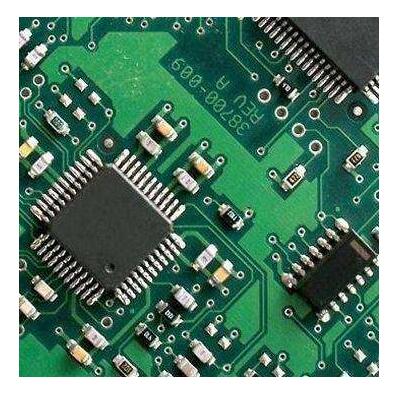
PCB board processing PCB board composition and its significance
PCB board consists of four layers, namely substrate, laminate, solder mask and screen printing. Substrate and laminate together define the basic electrical, mechanical, and thermal board properties.
substrate
Fiberglass FR4 is the most common material used for PCB substrates. In this case, FR stands for flame retardant. Fit because of its rigidity and thickness. For flexible PCBS, use Clapton or equivalent plastic.
The thickness of PCB board depends on its application or use. For example, most Spark fun products are 1.6mm thick, while Arduino Pro products are 0.8mm thick. PCBS made with cheaper materials such as epoxy resins lack durability.
Substrate is found in low-cost consumer electronics. These have low thermal stability, which causes them to lose lamination easily. The substrate also causes smoke when the soldering iron is held to the board for long periods of time, which makes them easy to identify.
The non-conductive layer of dielectric material is selected based on the dielectric constant.
The substrate must satisfy certain desired properties, such as the glass transition temperature (Cg). Cg is the point at which heat causes a material to deform or soften. A variety of materials can be used as substrates, such as aluminum or insulating metal substrates (IMS)FR-1 to FR-6, polytetrafluoron (PTFE), CIM-1 to CIM-5, G-10 and G-11, RF-35, polyimide, alumina and flexible substrates such as Pyramidal and Clapton.
"Overall, it minimizes thermal resistance and conducts heat more efficiently. These substrates are mechanically stronger than the thick film ceramic and directly bonded copper structures commonly used in many applications."
laminate
This provides properties such as coefficient of thermal expansion, tensile and shear strength, and Cg. Common mediums used for laminate are CIM-1 and CIM-3, FR-1, FR-4, Teflon (Teflon), FR-2 to FR-6, CIM-1 to CIM-5 and G-10.
Copper foil is the next layer laminated onto the board. For double-sided PCBS, copper is applied to both sides of the substrate. The thickness of copper varies according to the application. For example, high power applications are thicker than low power applications.
Welding resistance film
This is the top layer of copper foil. It can be used as insulation material for copper trace wires to prevent accidental contact with other conductive metals. It helps to weld in the right place.
It is a protective layer that prevents external contamination and provides the required isolation between surface elements such as pads, copper wire and boreholes.
Silk screen printing
Screen printing is overlaid on a solder stop layer and is used to add letters, numbers and symbols to the PCB for easy assembly and better understanding of the board through indicators.
Select PCB board according to PCB type
Boards can be classified in the following ways:
Component location: single - sided, double - sided and embedded
Stacking: Single and multiple layers
Design: Based on modules, customizations and specialities
Bendability: rigidity, flexibility and stiffness-flexibility
Strength: Electrical strength and mechanical strength
Electrical functions: High frequency, high power, high density and microwave
Circuit board type can be used to select the most suitable circuit board material for design.
A single-sided PCB consists only of a substrate with a thin copper coating. Place the protective solder mask over the copper layer. Screen printing coatings can be applied to the top to mark the elements of the board.
The substrate of a double-sided PCB consists of a metal conducting layer and components attached to both sides (top and bottom).
Multilayer PCBS increase the density and complexity of PCB designs by adding additional layers to those seen in double-sided PCB configurations. These allow for extremely thick and highly composite designs. The additional layer used is the power layer, which provides power to the circuit and reduces the level of electromagnetic interference (EMI).

Rigid PCBS use a strong rigid substrate material, such as fiberglass, to prevent the board from twisting. The mother board in a computer is the best example of a non-flexible PCB.
The substrate of flexible PCB is flexible plastic. It can be turned and shifted during use without damaging the circuit on the PCB. It can restore heavy wiring in advanced gears where weight and space are critical, such as satellites.
Rigid - flexible board consists of a rigid circuit board attached to a flexible circuit board. These panels can meet the composite design requirements as needed






