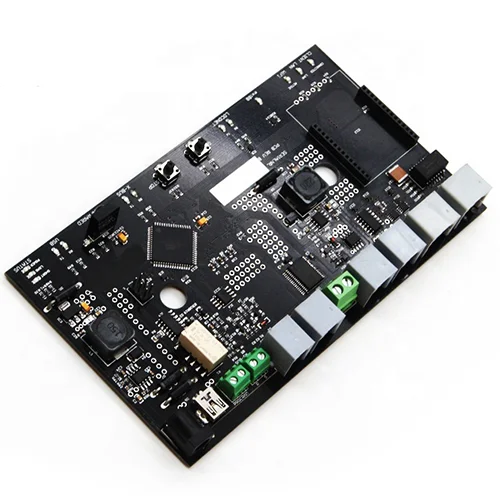
Wireless Charger PCB Assembly
Name: Wireless Charger PCB Assembly
Substrate: FR-4/High TG/Polyimild/PTFE/Rogers
Copper Thickness: 1/3OZ- 6OZ
Plate thickness: 0.21-6.0mm
minute. Hole size: 0.20mm
minute. Line width: 4 million
minute. Line spacing: 0.075 mm
Surface treatment: spray tin/gold drill/OSP/lead-free spray tin
Board size: minimum 10*15mm, maximum 508*889mm
Product Type: OEM&ODM
PCB standard: IPC-A-610 D/IPC-III standard
Certificate: ISO9001/ CE//TUV/ ROHS
Warranty: 1 year
Service: One-stop turnkey service
Electronic testing: 100%
Logistics: Air/Sea
A wireless charger refers to a charger that is connected to a terminal device that needs to be charged without a traditional charging power cord. It adopts the latest wireless charging technology. By using the magnetic field generated between the coils, it can magically transmit electric energy. Inductive coupling technology will Become a bridge connecting charging base stations and equipment.
Wireless charging technology obtained 20 patents in 2007, a variety of devices can use a charging base station, the wired charging of mobile phones, MP3 players, power tools and other power adapters will no longer exist.
Basic introduction
A wireless charger refers to a charger that is connected to a terminal device that needs to be charged without a traditional charging power cord. It adopts the latest wireless charging technology. The wireless charging technology obtained 20 patents in 2007. A variety of devices can use one Gone are the corded charging scenarios for charging base stations, cell phones, MP3 players, power tools and other power adapters. By using the magnetic field generated between the coils to magically transmit electrical energy, inductive coupling technology will become a bridge connecting charging base stations and devices. Most current chargers, such as iPods and iPhones, charge the device's built-in battery through direct contact with metal wires. The advantage of wireless charging technology lies in its convenience and versatility. The disadvantage is low efficiency and can only provide electric energy. Apple's Dock connector not only provides power, but also syncs audio and video files to the device via the USB interface. However, wireless charging technology will still bring improvements to WiFi and battery technology. For devices that do not require data transmission, this new technology will greatly reduce the number of various chargers that users need. In addition, by adopting wireless charging technology, public mobile device charging stations may become a reality.
Historical process
Historical discovery
Back in the 1830s, Michael Faraday discovered that changes in the surrounding magnetic field would induce an electric current in a wire. In the 1890s, the Serbian-born scientist Nikola Tesla applied for the first patent.
Unfortunately, research in this area was delayed for a century. The biggest obstacle is that the transmission efficiency is too low and there are dangers. Electromagnetic radiation is only suitable for transmitting information, not energy. Because radiation is non-directional, energy is wasted in useless space. The use of directed electromagnetic radiation, such as lasers, has been envisaged, but is impractical and extremely dangerous.
Subsequent development
Professor Xu Shuyuan, Department of Electronic Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, has successfully developed a "wireless battery charging platform" in the early years, which can put several electronic products on a charging platform without external wires, and automatically charge through low-frequency electromagnetic fields. The time is no different from conventional chargers. However, this technology still requires the product to be in contact with the charger, and it mainly uses the principle of near-field electromagnetic coupling.
Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology have made new progress in wirelessly transmitting electricity. They used a power source two meters away to light a 60-watt light bulb "separately"
In Soljacic's design, non-radiative wireless energy transmission has a distance limit, and the smaller the receiver, the shorter the distance. He calculated that a laptop-sized object could receive wireless power transfers over a range of a few meters, "so that installing a transmitter in each room could power laptops throughout a house."
Soljacic hopes to increase the efficiency to 70% to 80% by using different materials and improving technology. They believe the improved device could wirelessly charge laptops, mobile phones and other devices within three to five years.
Working principle
Physicists have long known that energy is efficiently transferred between two objects that resonate at the same frequency, while objects of different frequencies interact weakly. This is the reason why a singer sings that one of the bottles with different water volumes can be broken without affecting other bottles. It's like when you're on a swing, you just need to sit on it and let your drooping legs swing synchronously to bring power to the swing. Wireless charging technology takes advantage of this principle. Similarly, wireless charging technology also applies the principle of electromagnetic wave induction and related AC induction technology. It uses corresponding coils at the sending and receiving ends to send and receive induced AC signals for charging. Users only need to The charging device can be charged by placing it on a "tablet". This charging method has appeared on watches and razors in the past, but it could not effectively charge large-capacity lithium-ion batteries at that time. The schematic diagram of the wireless charger technology is shown in the figure.
A new type of wireless charger was originally invented by a British company. It looks like a plastic mouse pad. This "mouse pad" is equipped with a dense array of small coils, so it can generate a magnetic field and transmit energy to a dedicated charger. Electronics that receive coils and thus charge. The receiving coil is made of magnetic alloy wound with wire, and is similar in size and shape to chewing gum, so it can be easily attached to electronic equipment. Charge your phone etc. by placing it on the pad, and charge multiple devices at the same time. Charging technology has appeared before, but this new invention is more convenient and practical. As long as the receiving coil is attached to mobile phones and other devices, they can be charged anywhere on the "mouse pad", unlike some previous technologies that require precise positioning. Several devices are placed on the mat at the same time and can be charged at the same time. The magnetic field generated by the charger is very weak, which can charge the device but will not affect nearby credit cards, video tapes and other items that use magnetic recording data.
The wireless charging system mainly adopts the principle of electromagnetic induction, and realizes energy transmission through energy coupling through coils. As shown in the figure, when the system is working, the input terminal converts AC mains power into DC power through the full-bridge rectifier circuit, or directly supplies power to the system with 24V DC terminal.
After passing through the power management module, the output direct current is converted into high-frequency alternating current by the 2M active crystal oscillator and supplied to the primary winding. The energy is coupled through two inductive coils, and the current output by the secondary coil is converted into direct current by the receiving conversion circuit to charge the battery.
A changing magnetic field will produce a changing electric field, and a changing electric field will produce a changing magnetic field. Their magnitudes are related to their rate of change, and the rate of change of a sinusoidal function is another sinusoidal function, so electromagnetic waves can propagate, and induced voltage The generation of the coil is related to the change of the magnetic flux, so the changing magnetic field inside the coil generates an induced voltage, thus completing the charging process.
Mobile phone wireless charging is a relatively novel charging method. Its principle is actually very simple, that is, to separate the primary and secondary of ordinary transformers to achieve wireless purposes. Of course, the working rate of wireless charging is relatively high, and even the iron core can be discarded and the direct coil can achieve the function of energy transfer.
Basic Features
1. From a theoretical point of view, wireless charging technology is harmless to the safety of the human body. The resonance principle used in wireless charging is magnetic field resonance, which only transmits between coils that resonate at the same frequency, while other devices cannot accept the band. In addition, wireless charging technology The magnetic field used is itself harmless to the human body. But wireless charging technology is a new type of charging technology after all. Taking Maiyuanke’s wireless charger as an example, many people will worry that wireless charging technology will be the same as when Wi-Fi and mobile phone antenna poles first appeared. In fact, the technology itself is harmless. .
2. Maiyuan's wireless charging technology uses magnetic resonance to transmit charges in the electric and magnetic fields between the charger and the device, and the coil and capacitor form a resonance between the charger and the device.
3. Maiyuan said that this system can be widely used in the future, such as the charging area for electric vehicles and the power transmission for computer chips. The charging time required by the charging system developed by this technology is only one hundred and fifty times that of the current one.
4.Wired charging technology is higher. The conversion rate of Maiyuan wireless charging is several percentage points higher than that of wired charging. High conversion is also a key factor for the global application of wireless chargers. However, wireless charging technology is also limited by distance. For future development, it is necessary to solve the problem of precise positioning of the wave band and magnetic field range for long-distance transmission.
5. The core chip is one of the difficulties in the application of wireless charging technology in products. Precise radiation range control, magnetic field frequency, and other controls are all implemented by chips.
Problem Summary
Market application development bottleneck
1. The core wireless charging technology is not perfect
2. It is difficult to achieve long-distance transmission in the radiation area
3. The hardware requirements for long-distance positioning are too high
4. The height matching of magnetic field resonance can be controlled and small
5. The application range is limited and has not been extended
6. Market factors Developers are unwilling to vigorously carry out technology research and development due to consumer psychology
Radiation hazard
The MIT researchers say the body responds strongly to electric fields but barely to magnetic fields, so the system would not affect human health. However, this is only a speculation. Some researchers expressed concern about this view, and further experiments are needed before it can be applied to real life.
As an electronic charging product, the charger itself cannot avoid radiation, so it is inevitable for wireless chargers to have radiation. However, the power of the wireless charger is very small, the charging time is long, and the radiation produced is also small, so it should not cause great harm to people.
Unified port
In order to avoid unnecessary waste and generate more electronic waste, China is implementing unified standardization of mobile phone charger ports. But for wireless charging technology, this will be the most popular: not only mobile phones can be used, but digital cameras, iPhones, iPads, and notebooks can also share this charging device. Japan's Fujitsu is even poised to roll out a more advanced technology that would extend that success from portable electronics to charging electric vehicles. The ultimate goal of Fujitsu's move is to set up public "charging points" on the streets, which can provide more convenient 24-hour all-weather charging services for portable digital devices and electric vehicle users. In addition, wireless chargers are smarter and save energy. Although the efficiency of wireless charging equipment is about 70%, which is equal to that of wired charging equipment, it has an automatic shutdown function when fully charged to avoid unnecessary energy consumption. And the performance acceptance rate is constantly improving.
Mobile phone built-in charging receiver, and unified wireless charging standard
To realize wireless charging of mobile phones and other products, there must be two parts: the transmitter, which is connected to the power supply, is responsible for transmitting electric energy to a wide space; the receiver, which is generally installed on electronic products, is used to receive electric energy. Wireless charging technology has begun to be used in mobile phone products. Taking the iPhone as an example, wireless charging manufacturers have refitted it and installed a kind of "clothes" similar to "apple peel" ". As a wireless charging receiver, it appears in the form of adding a mobile phone charging case, but related modified products can be launched in China. Dubbed the "Qi Door," the case supports both iPhones and BlackBerrys, giving users an early access to the feature without having to replace their phones. In early 2013, the wireless charging receiver will be fully "slimmed down" and become a wireless charging receiving chip built into mobile phones, only as big as a fingernail. Nokia, Philips, LG, Samsung, Sony Ericsson, iPhone, HTC, Google, ZTE, Sharp, RIM and many other internationally renowned mobile phone manufacturers all support this technology, and wireless chargers may also be bundled with mobile phones for sale.
The key to wireless charging of mobile phones is compatibility, and the Qi standard can ensure brand compatibility
Wireless charging technology mainly uses electromagnetic technology. The transmitter converts the current into electromagnetic, and the mobile phone uses the built-in chip receiver to convert the electromagnetic into current to charge the mobile phone. The key to the promotion of wireless charging technology is to ensure that the wireless chargers of various manufacturers are compatible. The formulation of the Qi standard enables wireless charging to have a unified technical specification and ensures the compatibility of the same charger with multiple brands and products. Menno Treffers, chairman of the Wireless Charging Alliance, said that the Qi wireless charging standard uses electromagnetic induction technology, which is more efficient and safer than other technologies. The Qi wireless charging standard includes three aspects: interface, performance, and regulations. This is a considerable challenge to the popularization of wireless charging technology. Therefore, mobile phones that pass the Qi standard can be powered by any Qi-certified charging base station, base or other rechargeable devices. Wireless charging. Qi's first pre-requirement for devices is no higher than 5 watts, which may be a big limitation for some manufacturers who want laptops to also use wireless charging technology.
Manufacturers have launched Qi standard wireless charging products, and the market is extensive
The world's largest battery and portable lighting equipment manufacturer Energizer (Energizer) said that it will soon launch a wireless charger product that supports the Qi standard, and will first bring a new wireless charging experience to Apple iPhone3GS and Blackberry Blackberry Curve8900 users. At the same time, according to data provided by market research company iSuppli, the wireless charging equipment market reached a scale of 14 billion US dollars in 2013. Philips has already started making new phones that include wireless charging. The Philips X723 mobile phone has already appeared, and its mining is a 3.2-inch 240X400 screen with GPS and a 3-megapixel camera. The good news is that the machine comes standard with a wireless charger XeniumQ1 (Qi wireless charging alliance standard), but the specific launch time and price have not yet been disclosed.
Receive antenna
Although this article focuses on chargers, it also provides an overview of receiving antennas. Because this type of wireless charging device is essentially a transformer, the primary is installed in the charger, and the secondary is installed in the terminal.
Because the receiving antenna that does not match the charger will cause current fluctuations in the charging circuit, how to choose a good charging antenna?
First: The terminal antenna needs to be magnetically shielded
If the charging antenna is only a hollow coil, when nearby metal objects approach, it will cause eddy current, which will reduce the charging efficiency, prevent the energy of the charger from radiating out, increase the current, and cause the charger to heat up.
Second: The magnetic medium selected by the charger is divided into two categories: organic magnetic materials and inorganic magnetic materials.
The organic magnetic material can be made very thin and warped, which is suitable for bonding the back cover of the mobile phone and used in the mobile phone; the inorganic magnetic material is made of sintered ferrite, which is fragile and suitable for installation in large spaces.
Name: Wireless Charger PCB Assembly
Substrate: FR-4/High TG/Polyimild/PTFE/Rogers
Copper Thickness: 1/3OZ- 6OZ
Plate thickness: 0.21-6.0mm
minute. Hole size: 0.20mm
minute. Line width: 4 million
minute. Line spacing: 0.075 mm
Surface treatment: spray tin/gold drill/OSP/lead-free spray tin
Board size: minimum 10*15mm, maximum 508*889mm
Product Type: OEM&ODM
PCB standard: IPC-A-610 D/IPC-III standard
Certificate: ISO9001/ CE//TUV/ ROHS
Warranty: 1 year
Service: One-stop turnkey service
Electronic testing: 100%
Logistics: Air/Sea



